Type 0 OR Type 1 of the Condition and their Functions
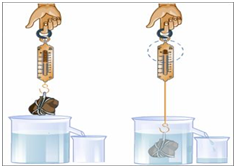
What kind of experiment does it illustrate?
Choisir la réponse correcte de la liste
Choose the right answer
An experiment in: ****
Read the passage below
Everyone knows that some objects float in water and that others do not. An object floats in water might sink in alcohol, and one that sinks in water might float in glycerine. All liquids possess in varying degrees the property that is called buoyancy an upward push upon objects that are submerged within them.
If you throw a piece of dry wood into a pond or a pool, the wood floats; the upward push of the water makes this possible .An object that sinks in water – like a piece of iron-weighs less when under water than in the air; this also is because the water exerts an upward pressure upon it. When you are taking a bath in a well-filled tub, you can raise your whole body easily by a slight pressure of your hands on the bottom of the tub. You could not do this so easily if you tried to raise yourself from the living-room floor because air is less buoyant than water.
Task 1: What is buoyancy according to the text?
- the ability of an object to float
- the power of a liquid to make an object float.
- a feeling of happiness and a belief that you can deal with problems easily
- BF the ability of prices, a business etc to quickly get back to a high level after a difficult period
Definition (b): Buoyancy is the power of a liquid to make an object float.
- What example is given to show the buoyancy effect?
- Is water more buoyant than air?
- ‘If you throw a piece of dry wood into a pond or a pool, the wood floats.’
- Yes, it is .
Analyse the following sentences:
- If you don’t hurry, you will miss the bus.
- If you throw a piece of dry wood into a pond or a pool, the wood floats.
- He may feel tired if he runs every day.
- If an angle is less than 90 degrees, we call it acute.
What we call these sentences? Why?
We call them conditional sentences. They start with the conjunction “if” which introduces a condition that may or may not happen.
The structure: If + condition clause, result clause.
Or
Result clause +if + condition clause.
- What tenses are used in the result clauses of sentences “a” and “b”?
- Result clause “a”: future simple (will miss) result “b”: present simple”floats”
- Which of the two results is true at any time because of its condition?
Sentence “b”: its result is scientifically proven and true at any time:
- If you throwwood into water, it floats.
- While sentence “a” the condition expresses a situation whose result is a prediction.
- You will missthe bus if you don’t hurry.
Order the sentences according to the degree of certainty expressed in their result clauses:
100%............................. 70%............................... 30%...................
- 100%: b) If you throw a piece of dry wood into a pond or a pool, the wood floats.
- d) If an angle isless than 90 degrees, we callit acute.
- 70%: a) You will missthe bus if you don’t hurry.
- 30% :c) He may feeltired if he runs every day. Or he can feeltired if he runs.
Type 0 of the conditional is used to talk about a situation whose result is a true fact or a scientific truth;therefore we can use :
- “when” or “whenever “instead of “if” .
- the result part is in the present simple.
If + subject + present simple, subject + present simple.
When + subject + present simple, subject + present simple.
- If you heat ice, it melts. → Ice melts if you heat it.
OR
When you heat ice, it melts.→ Ice meltswhen you heat it.
- If it rains, the grass gets wet. → The grass gets wet if it rains.
When it rains, the grass gets wet. → The grass gets wet when it rains.
Type 1 of the conditional is to make a real hypothesis whose result is probable or possible, it is not a scientific truth, it is a prediction; therefore, we use:
- The future simplein the result part when the result is very probable.
If I miss the bus, I will takea taxi.
- “may” or “can” in the result part when the result is possible.
- If you arrive early, you may seeher.
- If she looks for a job, she can finda good position
- To give advice:
If you feel tired, take a holiday.
→ If + subject + present simple, + imperative .
Or
You should goand see a doctor if you feel sick.
- To make an offer:
I will waitfor you if you want.
- To make promises:
If you stay here, I will workharder.
- To express threat:
I will not speakto you if you don’t apologizeto her.
- To express warning:
If you don’t walkcarefully, you will falldown and break your leg.
- إختبارات
- 10
- الأجوبة الصحيحة
- False
- الأجوبة الخاطئة
- False
- مجموع النقاط
- False
المراتب الخمس الأولى في Quiz
- Wā Mår
- 112 نقطة
-

المراتب الخمس الأولى في التمارين
- hadjer kadrine
- 1 نقطة
-

- None None
- 0 نقطة
-

- Serine Laouamer
- 0 نقطة
-

- Rah Ra
- 0 نقطة
-

- Yola Kim
- 0 نقطة
-










