Reporting

The following solidarity activities, the most frequent ones amongst the young people interviewed, are related with the money donated to countries or people who need it (48%) and the more or less specific collaboration in solidarity actions –helping neighbours, protection of the environment, etc- (39%). The group of young people who say they have collaborated in solidarity actions when extraordinary events have occurred – wars, natural disasters, etc. - (34%) is smaller; together with those people who spend some of their leisure time helping other people (29%) and those who say they attend fund-raising concerts (26%). There are still fewer people who are blood donors (15%).
Choisir la réponse correcte de la liste
Choose the right answer:
- The text is a report of a survey.****
- It deals with young people and solidarity.****
- None of them gave money.****
- Most of them donate their blood.****
3.False.
Most of the young people interviewed are related with the money donated to countries or people who need it.
4. False:
Fewer people are blood donors, representing 15% of the informants.
39% of young people say that they have collaborated in solidarity actions when extraordinary events have occurred – wars, natural disasters
A. Which tense are the verbs in reported statement of the report
Key: the present perfect simple
B. Which verb is used to report the statement?
Key: “say” is the reporting verb.
|
Direct statement |
Reported statement |
|
1.’We have collaborated with solidarity actions when extraordinary events have occurred,’ they say.
2. ’We have collaborated with solidarity when extraordinary events have occurred,’ they said.
|
They say that they have collaborated with Solidarity actions when extraordinary events have occurred.
They said that they had collaborated with Solidarity when extraordinary events had occurred. |
- Reporting affirmative and negative sentences
When reporting such statements we use the reporting verbs “to say that” and “to tell someone that."
when the reporting verb is in the present tense or the present perfect simple ,the tense of the direct speech does not change once reported.
“I don’t understand, ’he says/ he has said.
He says/ has said that he doesn’t understand.
HOWEVER, when the reporting verb is in the past tense, the tense of the direct speech must change once reported.
- "I don’t understand,”he said→ He said that he did not understand.
- "We have alreadydonated some blood,”they told the reporter.
- They told the reporter that they had already donatedsome blood.
When the reporting verb is in the past tense, there are changes to make in tenses.
|
Direct Speech |
Reported Speech |
|
‘We work every day,’they said.
Present simple |
They said that they worked every day. Past simple |
|
‘We have workedevery day,’ they said. Present perfect simple |
They said that they had workedevery day. Past perfect simple |
|
‘We worked yesterday,’ they said. Past simple |
They said that they had workedthe day before Past perfect simple |
|
‘We had workedbefore,’ they said. They said Past perfect simple |
They saidthat they had workedbefore. Past perfect simple |
|
‘We are working,’ they said. |
They said that they were working. |
|
‘They will work,’ they said. Future simple |
They said they would work. The conditional |
|
Direct Speech |
Reported Speech |
|
“am” / “is” |
was |
|
“are” |
were |
|
“was”/” were” |
Had been |
|
“has/have” |
Had |
|
“ Must “ |
Had to |
|
“May” |
Might |
|
“can” |
could |
|
“will” |
would |
|
“shall” |
should |
- Even time adverbs, demonstratives and adverb of place change in case the reporting verbs is in the past tense.
a)Demonstrative pronouns this and these
“This” used in time expressions usually becomes “that”
‘She is coming this week, ’he said. →He said that she was comingthat week.
However,”this” and “that” used as adjectives usually change to “the”
‘I bought this pearl/these pearls for my mother,’ he said.
→He said that he had bought the pearl /the pearls for his mother.
“This, these”used as pronouns can become “it, they/them”
‘I foundthese in the kitchen’ he said.
→He said that he had found them in the kitchen.
‘We will discussthistomorrow,’ he said.
He said that they would discussitthe next day.
|
Reported speech |
Direct speech |
|
That day The day before Two days before The next day/the following day In two days’ time The following week/year The previous week/year A year before/the previous year
Now /then |
Today Yesterday The day before yesterday Tomorrow The day after tomorrow Next week/year Last week/year A year ago
NB. Now |
“Here” becomes “there” but only when it is clear what place is meant:
‘I willbe hereagain ,’ he said→ He said that he would be there
A question becomes an affirmative sentence once reported and the punctuation changes as well.
‘Where do you go?’ he asks. → He asks me where I go.
‘Question word+ auxiliary +subject +verb?’ he asks.
→ He asks me where I go.
→ He asks me question word+ subject +verb.
There are two types of questions:
1. WH-questions 2.Yes /No questions
The reporting verbs are:
” to ask someone and to want to know” and they obey the same rules as affirmative statements.
1. WH-questions
a.1.”Why did Jones try to get into the house? ”she asked.
. 2. She wanted to know why Jones had tried to get into the house
b.1. ”How long ago did your neighbours leave their house?” asked the police –officer.
2. He wanted to know how long ago her neighbours had left their house.
2. Yes /no questions
A.1.”Must you go now?” he asked her.
2.He wanted to know if she had to go now
B.1.”Do you live in the city? ”she asked me.
2. She wanted to know whether I lived in the city.
N.B. We can use “whether” instead of “if”
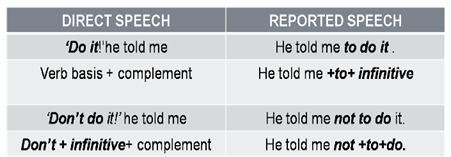
Today we tend to put a full stop at the end of a command. However, we can always use an exclamation for emphasis.
We report advice, requests and warnings in the same way as commands except for suggestions.
|
Function |
Direct speech |
Reported speech |
|
Advice
Requests
Warnings
Suggestions
|
‘You ought to be patient, ‘she advised me. Or ‘If I were you , I would be patient,’ she advised me.
‘Could you explain to me your idea, please?’ I asked him.
‘Don’t swim out too far,boys’ she warned the boys.
‘Let’s have a stroll in the park,’ she suggested. |
She advised me to be patient.
I asked him to explain to me his idea.
She warned the boys not to swim out too far.
She suggested having a stroll. |
|
Function |
Direct speech |
Reported speech |
|
Advice
Requests
Warnings
Suggestions
|
Affirmative form -‘ Subject+ ought to +base form, ‘ he advised me.
-‘ If I were you, I would +base form, ‘ he advised me.
Negative form
‘ Yous houldn’t +base form, ‘he advised me.
-‘ Can/could+you+base form ,please ? ‘ he asked me. ‘ Would you mind +you+verb+ing ? ‘ he asked me.
Affirmative
‘ Bareform+complement ! ‘ he warned me.
Negative form
‘Don’t +base form+ complement !’ he warned me.
‘Let ‘s +base form’,he suggested.
‘ How about +verb +ing… ?’ he suggested |
He advised me +to+ base form.
He advised me not to+ base form
He asked me to+base form.
He warned me to+base form +complement.
He warned me not to +base form+ complement.
He suggested + verb+ ing. |
- إختبارات
- 9
- الأجوبة الصحيحة
- False
- الأجوبة الخاطئة
- False
- مجموع النقاط
- False
المراتب الخمس الأولى في Quiz
- Kessous Nivine
- 152 نقطة
-

المراتب الخمس الأولى في التمارين
- imene benallou
- 4 نقطة
-

- raouf boudriga
- 4 نقطة
-

- موو موني
- 4 نقطة
-

- meriem kaoukaou
- 4 نقطة
-

- lys linden
- 4 نقطة
-










